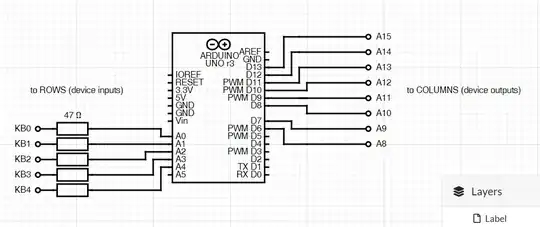
 This is a kind of an experiment, I just have a question on how Arduino ports work. Consider this sample: there is this target device that I'm trying to control with Arduino. The device uses a typical scanned keyboard (8 output columns and 5 input rows which make contact whenever a user presses a key). I am trying to emulate that keyboard with Arduino. Of course, a standard way to do it would be to read 8 columns and produce appropriate output on the 5 rows. However, Arduino is not fast enough to make it work. So, I am going with multiplexer idea. 8 Arduino's digital pins are connected to columns and 5 Arduino digital pins are connected to rows. GND rail is NOT connected.
This is a kind of an experiment, I just have a question on how Arduino ports work. Consider this sample: there is this target device that I'm trying to control with Arduino. The device uses a typical scanned keyboard (8 output columns and 5 input rows which make contact whenever a user presses a key). I am trying to emulate that keyboard with Arduino. Of course, a standard way to do it would be to read 8 columns and produce appropriate output on the 5 rows. However, Arduino is not fast enough to make it work. So, I am going with multiplexer idea. 8 Arduino's digital pins are connected to columns and 5 Arduino digital pins are connected to rows. GND rail is NOT connected.
So the idea is this. By default all Arduino pins are set to INPUT in init() routine. Whenever I need to emulate a key press, I just set a corresponding row pin to OUTPUT and LOW, same for the column pin. So, that should work as some kind of a multiplexer, since Arduino pins are driven by Mosfets and input state is high impedance, and during output state both pins would be tied to Arduino's GND which makes a hardlink connection between them (setting to HIGH should work to, there's no difference).
Here is the test code which should make a keypress every 5 seconds:
pinMode(ROW0_PIN,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(ROW0_PIN,LOW);
pinMode(COLUMN0_PIN,OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(COLUMN0_PIN,LOW);
Sleep(5000);
pinMode(ROW0_PIN,INPUT);
pinMode(COLUMN0_PIN,INPUT);
Sleep(5000);
Now, the thing IS working. However, it only works if one column pin is connected. When I connect any two pins, the target device stops responding. What I found is that actually, when I do
pinMode(COLUMN0_PIN,OUTPUT);digitalWrite(COLUMN0_PIN,LOW);,
the neighboring pins somehow get activated too, which results in all column outputs connected together and sending signal to row inputs.
If all pins are set to INPUT, it works fine, meaning, no connection between rows and columns.
My qustion is: why is it happening? Let me rephraze it: somehow setting a digital pin to OUTPUT makes other digital pins lose their high impedance state, although all of them are set to input. I haven't checked if this is happening within a hardware port or not, just consider schematics, please.