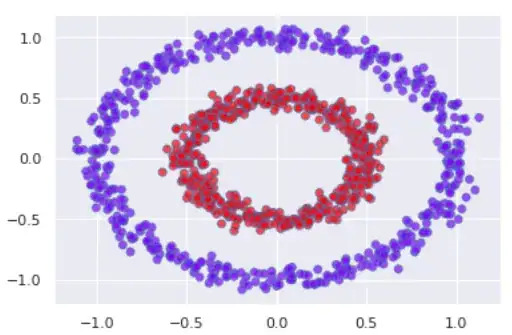
I have understood why k-means can get stuck in local minima. Now, I am curious to know how the spectral k-means helps to avoid this local minima problem.
According to this paper A tutorial on Spectral, The spectral algorithm goes in the following way
Project data into $R^n$ matrix
Define an Affinity matrix A , using a Gaussian Kernel K or an
Adjacency matrixConstruct the Graph Laplacian from A (i.e. decide on a normalization)
Solve the Eigenvalue problem
Select k eigenvectors corresponding to the k lowest (or highest) eigenvalues to define a k-dimensional subspace
Form clusters in this subspace using k-means
In step 6, it is using k-means. How is it overcoming the local minima problem of k-means? Moreover, what are the benefits of spectral over k-means?
If someone gives detailed insight upon this, it will be very helpful for me.