Multi-class Confusion Matrix is very well established in literature; you could find it easily on your own. Anyhow, Scikit-learn can do it easily like:
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
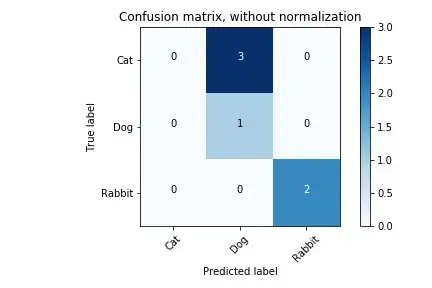
y_true = ['Cat', 'Dog', 'Rabbit', 'Cat', 'Cat', 'Rabbit']
y_pred = ['Dog', 'Dog', 'Rabbit', 'Dog', 'Dog', 'Rabbit']
classes=['Cat', 'Dog', 'Rabbit']
confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred, labels=['Cat', 'Dog', 'Rabbit'])
array([[0, 3, 0],
[0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 2]])
You can even plot it nicely using the below function:
def plot_confusion_matrix(cm, classes,
normalize=False,
title='Confusion matrix',
cmap=plt.cm.Blues):
"""
This function prints and plots the confusion matrix.
Normalization can be applied by setting `normalize=True`.
"""
import itertools
if normalize:
cm = cm.astype('float') / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
print("Normalized confusion matrix")
else:
print('Confusion matrix, without normalization')
print(cm)
plt.imshow(cm, interpolation='nearest', cmap=cmap)
plt.title(title)
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(classes))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, classes, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, classes)
fmt = '.2f' if normalize else 'd'
thresh = cm.max() / 2.
for i, j in itertools.product(range(cm.shape[0]), range(cm.shape[1])):
plt.text(j, i, format(cm[i, j], fmt),
horizontalalignment="center",
color="white" if cm[i, j] > thresh else "black")
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
plt.tight_layout()
like this:
cnf_matrix = confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred,labels=['Cat', 'Dog', 'Rabbit'])
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
# Plot non-normalized confusion matrix
plt.figure()
plot_confusion_matrix(cnf_matrix, classes=['Cat', 'Dog', 'Rabbit'],
title='Confusion matrix, without normalization')
More examples here and here.
