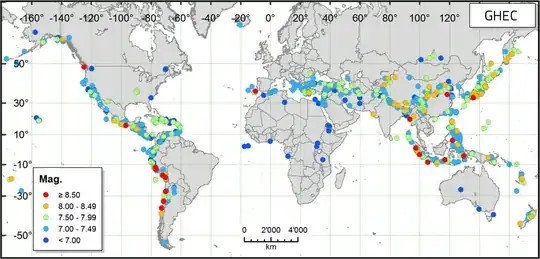
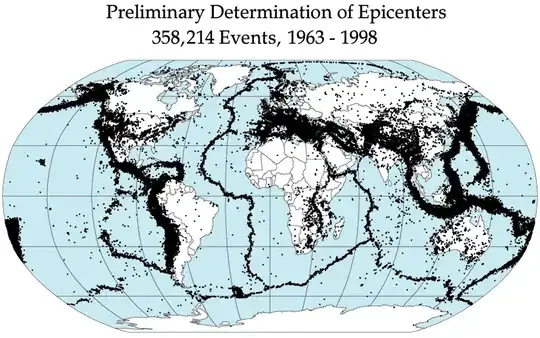
Most earthquakes happen at the edges of the Earth's tectonic plates. Look at a better sample of earthquake epicenters collected using modern seismological techniques and compare to this List of tectonic plates
Earthquake epicenters are concentrated at the edges, and more sparse in plate interiors, but there are regions of high seismicity at high and low latitudes.
If you really want to know whether the concentration of earthquake epicenters is greater near the equator than near the poles, then you should try the following:
1) Divide the surface of the globe into ~30 regions of equal area.
2) Make a table with a row for each region. Give the table two columns: the region's latitude (L), and the number of epicenters in the region (E).
3) Compute the arithmetic average of E for all 30 regions, call this G. Take the square-root of G and call this D.
4) Now look at your table. How many regions have a concentration E>5*G? How many of these are located at 'polar' latitudes and how many are located at 'equatorial' latitudes?
5) If you find that 80% or more of the E>5*G regions are in 'equatorial' regions, then that is probably evidence that significantly more earthquakes are measured in 'equatorial' regions. If you don't find this much, the effect is small.