Motors for electric bikes may be brushed, or they may be brushless DC motors (BLDC motors). The industry default has become brushless motors, because generally they are quieter, smaller, and lighter, and they don't need to serviced.
Basically, what happens is thick copper coils of wire electric power from the battery into the movement that pushes you along. Instead of having one motor powering all the wheels using gears or chains, they build a motor directly into the hub of each wheel—so the motors and wheels are one and the same thing.
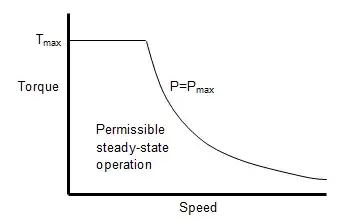
Now due to the availability of high torque over wide range of motor speed directly coupling the motor with the motor is not a great idea. Thus, generally the electric motor is always connected to the drive wheel through fixed gear reduction ratio. for this purpose, we generally use a combination of spur gears or helical gears in order to incorporate the advantages of regenerative breaking (charging of battery during breaking or when no throttle is applied / dynamo) which is an essential requirement for all electrical vehicle.
for the other part of your question
From basic physics, power is defined as rate of energy consumption. In electrical engineering load is defined as power but also at particular voltage & frequency. You often find the heaters are rated as 1.2 kW at 250 Volt that means it will consume 1200 watt if supplied from 250 volt, and if the voltage is less than 250 volts then its power won’t be 1200 watt. similarly, motor is rated to give full load output when connected the source of specified voltage and frequency.