If the piston is in (slight) clearance inside the cylinder, it's a bit like calculating the flow rate through a capillary, with the difference in diameter being the capillary diameter and the contact length between the piston and the cylinder the capillary length. There are various online calculators to help you with the actual calculation, such as this one. If you're after the theory, it's based on Bernoulli's principle.
EDIT
The length doesn't actually come into account in Bernoulli's equation, only the pressure and flow rate, if you neglect the difference in altitude. If you want to take account of the length, then you also need to look at the friction and things start to get messy. The most common approach is generally the Darcy-Weisbach equation. It's expressed as pressure loss, but you can rearrange the equation to work out the fluid velocity and therefore the flow rate. Careful which friction factor you use, the Darcy factor is 4 times the so-called Fanning friction factor. For laminar flow, it is generally approximated as $\frac{64}{R_e}$ where $R_e$ is the Reynolds number.
The air properties are also dependent on pressure and temperature, but assuming dry air at ambient temperature at standard atmospheric pressure (not exactly true, but it won't be far off) and a pressure drop of 1 bar between the piston chamber and the atmosphere, I get a flow rate of ~20.4 mL/min with a 1mm length and ~1.7mL/min with a 12mm length. I checked a posteriori that the assumption of laminar flow was valid.
Darcy-Weisbach equation
Pressure loss form:
$\Delta P = f_D * \frac{L}{D} * \frac{\rho u^2}{2}$
Re-arrange to give flow rate, given that $Q = A * u$
$Q = A * \sqrt{\frac{2}{\rho} * \frac{\Delta P * D}{f_D * L}}$
Friction factor
Assume flow is laminar (need to check a posteriori):
$f_D = \frac{64}{R_e} = 64 * \frac{\nu A}{QD}$
which gives (using $\nu = \mu / \rho$):
$Q = \frac{A * \Delta P * D^2}{L} * \frac{1}{32 \mu}$
Numerical application
D = 0.04e-3; % [m], diameter
L = 1e-3; % [m], length
dP = 1e5; % [Pa], pressure difference
mu = 1.846e-5; % [kg/(m*s)], dynamic viscosity of dry air at 1atm and 300K
rho = 1.2922; % [kg/m^3], air density at standard conditions for P and T
A = pi*D^2/4; % [m^2], cross area
Q = A*dP*D^2/(L*32*mu); % [m^3/s], flow rate
Re = Q*D/(A*(mu/rho)); % [-], Reynolds number
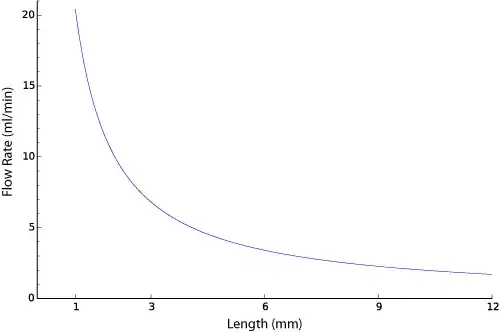
This gives a flow rate of ~20.4 ml/min and a Reynolds number of ~758, which is less than 2000, so the assumption of laminar flow is valid.
Change the length to 12mm, and you get a flow rate of ~1.7 ml/min and a Reynolds number of ~63.
