I have a flat piece of wood shaped like this: 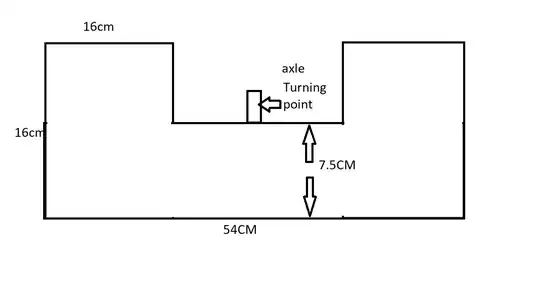 And it is turning around axle.
What i would like to know is, if it is rotated e.g. at 1000 RPM, how much power would that take?
And it is turning around axle.
What i would like to know is, if it is rotated e.g. at 1000 RPM, how much power would that take?
I know that drag force should be equal to this: $$ F_D=\frac{1}{2}C_D\rho_{air}Av^2 $$ And power:
P = Fd ⋅ v
I am using P air = 1.2 and Cd = 1.1 (i don't know if this is correct) .
First i calculated speed based on outer radius(27cm), but because of V^2 that was a big mistake, now i have split horizontally (or vertically if you are watching the picture) in parts of 0.5cm, and then calculated power for each part individually and then add them together, but i am getting what i think is lower value than what it should be (in range of 150-200W), i am getting ~87W at 660RPM. I am guessing i have a wrong approach to this problem.
EDIT 1: Here is python code how i calculated power with my way and also with Yaniv way.
RPM = 500
RPS = RPM / 60
def estimatedPower(RPS): # RPS = revolution per second
finalPower = 0
forceSmallPiece = 0
forceBiggerPiece = 0
for i in range(0, 54):
radius = i/2
if radius > 11:
A = 0.0008
V = radius/100*2*3.1415 * RPS
F = (1.1*1.2*A*V*V)/2
forceBiggerPiece += F
else:
A = 0.000375
V = radius/100*2*3.1415 * RPS
F = (1.1*1.2*A*V*V)/2
forceSmallPiece += F
P = F * V
finalPower += P*2 # *2 is because there are 2 blades
print("power: ",finalPower)
return finalPower, forceSmallPiece, forceBiggerPiece
finalPower, forceSmallPiece, forceBiggerPiece = estimatedPower(RPS)
AngularSpeed = RPM * 2 * 3.1415/60
Fd = forceBiggerPiece
Fd1 = forceSmallPiece
torque1 = Fd * 0.19
torque2 = Fd1 * 0.055
torque = (torque1 + torque2) * 2 # *2 because there are 2 fan blades
p = torque * AngularSpeed
print("Power with torque: ",p)