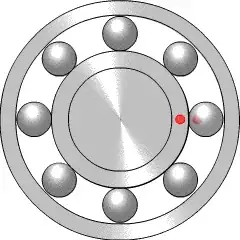
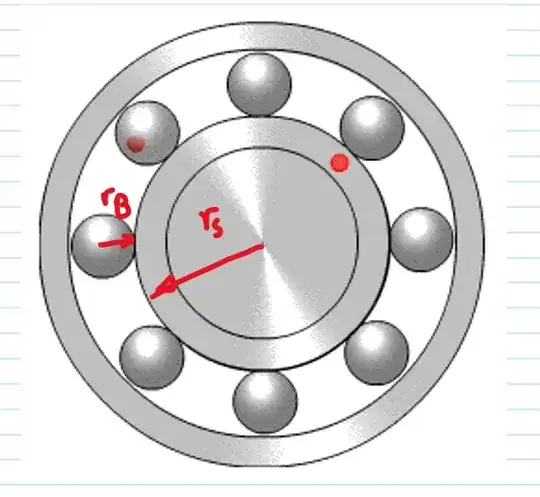
Assuming no slip between the inner race and the outer race of a ball bearing, what is the entrainment speed between the balls and the inner race? The inner race is rotating at $\omega_i$ and the outer race is fixed, $\omega_o = 0$, as shown below:
I know the entrainment speed is
$$ \bar{v} = \frac{1}{2}(\vec{V_1} + \vec{V_2}) - \vec{V_0} $$
I am having difficulty in calculating the velocity of the balls compared to the inner race using cross products and understanding how this relates to the entrainment speed equation.
The inner race has radius, $R_i$
The outer radius has radius, $R_o$
The balls have radius, $r$